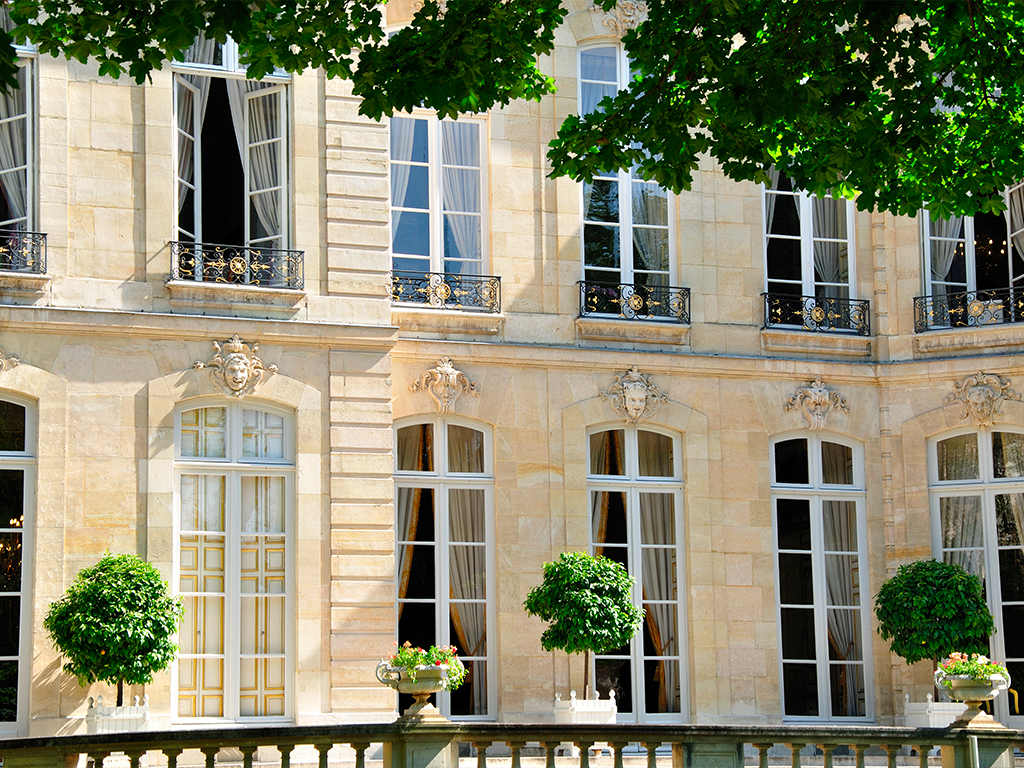
The term "private mansion" refers to a large urban residence owned by a wealthy individual or noble family. This type of architecture is typical in France and has its roots in the medieval period. Private mansions are often considered architectural masterpieces that showcase French prestige and refinement. In this article, we will explore the characteristics, architectural styles, and the most beautiful examples of private mansions in France.
Characteristics of Private Mansions
Firstly, it is important to define what a private mansion is. It is an individual residence, often built on multiple floors, occupied by a single affluent family. The size and layout of these mansions vary depending on the time period and region. Some private mansions were designed to be secondary residences, while others were intended to be main residences.
Exterior and Interior Spaces
A key element of private mansion architecture lies in their exterior design: these residences generally have a garden or a enclosed courtyard, providing a private green space for their occupants. The landscaping can take the form of a French-style garden or an English garden, depending on the owner's taste and the construction era.
Inside, a private mansion is characterized by spacious rooms with harmonious proportions, often featuring high ceilings, large windows, and refined decoration. The materials used are noble and varied: carved woodwork, marble, stucco, gilding, etc. The rooms can be arranged in an enfilade, meaning that they connect with each other to create a coherent and pleasant visual journey.
Architectural Styles of Private Mansions
The architecture of private mansions has evolved over time, reflecting the artistic and cultural trends of each period. Thus, there are different architectural styles characteristic of these mansions. Among them:
Medieval Private Mansions
The first grand private mansions appeared in the 14th century in certain French cities, particularly in Paris. Their facades were then punctuated by regular bays and mullioned windows. The ornamentation was still relatively modest, but the interiors already showed a search for comfort and aesthetics. An emblematic example is the Hôtel de Cluny in Paris, which now houses the National Museum of the Middle Ages.
Renaissance Private Mansions
In the 16th century, the Italian influence and the architectural discoveries of the Renaissance made their mark in France and left a lasting aesthetic impact on private mansions. The facades became more monumental and often featured sculpted elements, such as columns, pediments, and balconies. A remarkable example is the Hôtel d'Assezat in Toulouse, a residence built by architect Nicolas Bachelier, inspired by Italian models.
Classical Private Mansions
The 17th century saw the establishment of the French classical style in the architecture of private mansions. The facades became more rigorously symmetrical and balanced, with a regular arrangement of openings. The ornamentation was also more controlled and sober, favoring the purity of lines over sumptuous decorations. Among the masterpieces of this period, we can mention the Hôtel Lambert on the Île Saint-Louis in Paris, designed by Louis Le Vau.
Rococo and Neoclassical Private Mansions
The evolution of architectural art in the 18th century led to private mansions with varied styles ranging from Rococo to Neoclassical. The facades presented a greater variety of materials and motifs, with plays of light and shadow highlighted by reliefs that evoke the French sense of taste. The Palais Rohan in Bordeaux is a representative example.
In conclusion, French private mansions reflect the architectural heritage of the country, with varied styles that have evolved over the centuries. These prestigious residences showcase French excellence in architecture, with their spacious rooms, elegant facades, and meticulously maintained gardens. Their historical and artistic richness is a source of pride for France and invites exploration of these architectural treasures.